PUBLIC CLOUD
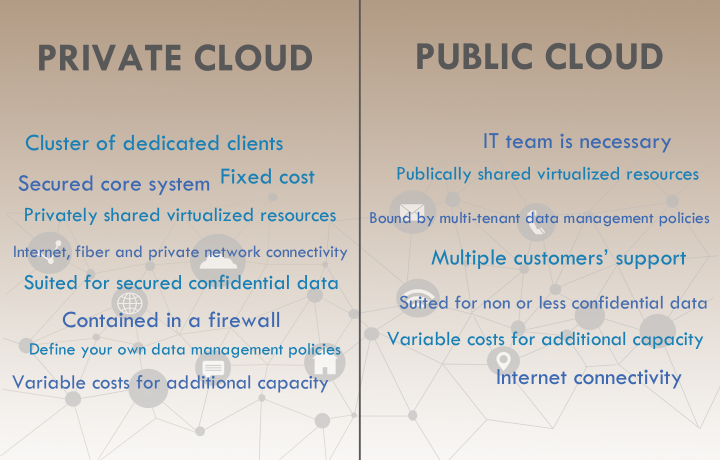
A public cloud is based on shared virtualized resources. It’s owned and operated by a service provider. It works with internet connectivity only, so it’s a multiple customers’ support. The first advantage of the public cloud is the speed with which you can deploy IT resources, you can stagger compute power up and down as your business needs in a few minutes. The second, is the ability to pay only for the resources used. Moreover, it can be cheaper for the users to set up because hardware, application and bandwidth costs are covered by the provider.
But there are also some disadvantages and public clouds may not be the right fit for every company. Because of the shared resources, this cloud is more vulnerable and there is less security for sensitive or confidential data. This model can also limit configuration or SLA specificity. The short-term cost saving could turn into a long-term big issue, so your IT department has to take extra time to ensure governance and security issues are well planned.
PRIVATE CLOUD
A private cloud is maintained on a private network. It’s hosted either on-site or in a service company’s data center. This cloud is dedicated completely to your business. It delivers the agility and the efficiency of the public cloud but also security, control and protection of your data. Moreover, it’s personalized, so you can customize the storage, or the networking components to fit to your specific IT requirements. The provider delivers flexibility, monitoring, security, and personalized service.
There is a limit, it can be more expensive than the public cloud, because it requires the company to still purchase and maintain all the software, equipment and infrastructure.
HYBRID CLOUD
As it’s called, the hybrid cloud permits you to combine public cloud with private cloud, and to get the best of both. By using this cloud, you can maintain control of a managed private cloud and rely on the public cloud as needed: use the public cloud for non-sensitive data and operations, and use the private cloud for confidential data. Moreover, during peak periods, applications can be migrated to the public cloud to fit to your needs at the T time. It’s highly flexible, cost-effective, secured and agile.
The disadvantage of this solution is the number of different security platforms because you have to ensure that all elements of your business can communicate with each other. Moreover, it’s more convoluted to manage this type of cloud as you’ll have to get more capabilities to manage public, private, and traditional datacenters together.